Colour is the perceivable characteristic of light; light is energy, so colour is a form of energy. In 1666 Sir Isaac Newton discovered that sunlight is a mixture of colours by noticing that when a ray of light passes through a prism, it is dispersed into its seven constituent colours: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. We see different colours because some objects reflect/absorb specific wavelengths. Human eyes perceive these wavelengths as colours.

Understanding colour
In web design colours are very subjective; take black for example, for some it is the colour of elegance, and it sometimes gives the idea of prosperity (you may immediately imagine a black and elegant limousine), but for others it can be a reminder of something unpleasant (death, hopelessness, evil, mourning).
You can’t use only a single colour in your work even if it is a site, logo or a business card. It needs to be a combination of two or more colours to be effective. Unfortunately making a wise mixture poses a tough choice; the modern monitor displays can render more than 16 million (16,000,000) colours. Therefore it’s very easy to make a wrong choice.
To combat these situations, designers and in particular web designers, have an important and useful guide to colour theory. This is a set of principles that help create harmonious colour combinations.
Primary colours
In traditional colour theory, there are only three colours which can’t be formed by combining others, to be more specific there are only three colours from which all the rest are created. These colours are: red, yellow and blue – primary colours.
Secondary colours
In traditional colour theory, there are only three colours which can’t be formed by combining others, to be more specific there are only three colours from which all the rest are created. These colours are: red, yellow and blue – primary colours.
Tertiary colours
In traditional colour theory, there are only three colours which can’t be formed by combining others, to be more specific there are only three colours from which all the rest are created. These colours are: red, yellow and blue – primary colours.

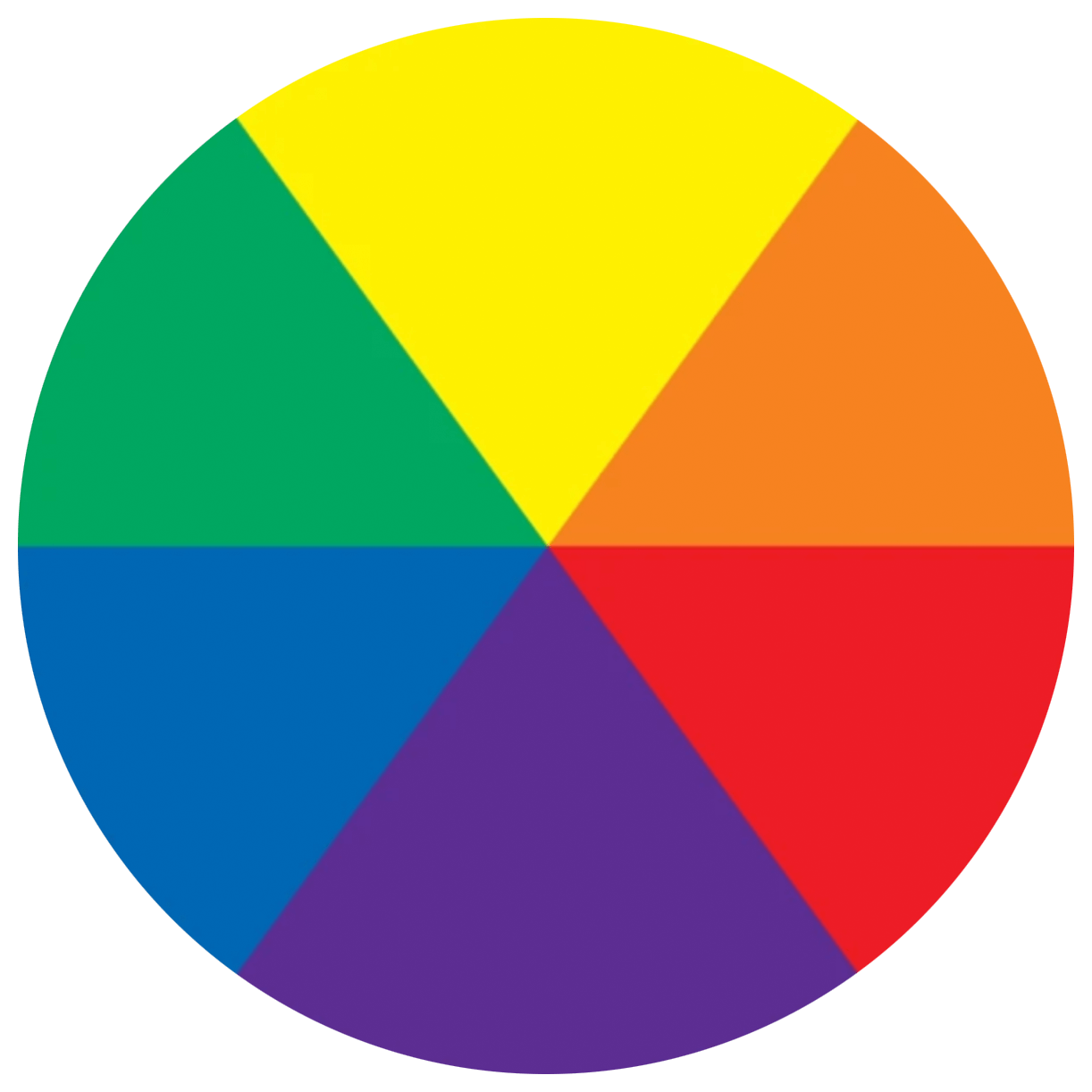
Cool & Warm colours
As in life, harmony consists of a well balanced arrangement of the parts. To establish some relationships between colours in colour theory we distinguish two categories:
- Warm colours are the colours from red to yellow including brown, orange, pink. These colours evoke warmth because they remind us of things like the sun or fire. These tend to advance in space.
- Cool colours are from green to blue, but also include some shades of violet. Cool colours are better for backgrounds and will give the impression of calm and reduce tension.
- White, black and gray are considered to be neutral.
Useful colour Theory Terms
These terms are very useful in colour theory too:
- Colour value: measures lightness or darkness of a colour.
- Saturation or intensity: is the brightness or dullness of a colour.
- Chroma: is how pure a hue is in relation to gray.
- Shade: a hue produced by the addition of black.
- Tint: a hue produced by the addition of white.
We use different sets of primary colours, the widest used being:
- RGB colour: this is based upon light. “RGB” stands for Red, Green and Blue (are the primary colours with green replacing yellow). Computer monitors and TV sets use RGB, but not used in printing.
- CMYK colour: this is based upon pigments. “CYMK” stands for Cyan, Yellow, Magenta and Black (K stands for black).Using these four colours most of the others can be achieved. CMYK can produce less colours than RGB (yellow-greens sometimes doesn’t have the best quality).This system is used in printing.
- Pantone (PMS) Colour: this is another system used in printing; PMS stands for Pantone Matching System and is a very large list of colour mixtures made by the Pantone Corporation. Unfortunately they are very expensive.
- Hexachrome: more recently Pantone developed another system, based on the regular cyan, yellow, magenta, black and in addition Pantone Hexacrome Orange and Pantone Hexacrome Green. It will be used and it is used in printing, being a step further than PMS or CMYK.
The Meaning of colour
Have you ever asked yourself why Las Vegas is the city of red neon? This is because red makes people take riskier actions than blue, that calms down the spirit. Scientists demonstrated that colours have an impact on the human brain. Thus a human being exposed to a certain colour can have different reactions, some are excitant, and others increase appetite or give the feeling of warmth or coolness.
Like we mentioned previously, colours are subjective and for each of us a colour has an individual impact, but generally accepted meaning of these are as follows:
- Black: mystery, elegance, death, evil, power, mourning.
- Blue: sadness, calm, loyalty.
- Green: abundance, nature, freshness.
- Yellow: happiness, concentration, hope.
- Red: passion, anger, danger, love.
- White: purity, cleanness, innocence.
- Purple: royalty, luxury, wealth, sophistication.
- Cream: elegance, purity.
- Gray: conservative, formality.
colours can be a great friend don’t forget that colour is light, light is energy, so colour is energy.
*Edited from original article






